Can You Register Your Vehicle For One Year At A Time In Maryland
Self-driving cars: your complete guide to autonomous vehicles

Self-driving car technology is advancing every day, and it'due south only a matter of time before fully driverless vehicles appear on public streets.
About daily, at that place'due south a new development in the driverless automobile space, and nearly every major car manufacturer, ride-sharing service and tech company from Apple to Google has bought into the driverless machine industry.
And, if you have all the driverless car churr at confront value, we're just a couple years away from a utopian society where cars volition navigate and park by themselves, and accidents become a rarity.
In fact, Google wants to take a self-driving ride-hailing service on the road by the end of this yr. Apple tree cocky-driving cars, meanwhile, are spotted regularly, driving down the road with rigs housing everything that's needed to run a cocky-driving experience.
While the driverless auto industry continues to abound, one unfortunate turn in the journey of self-driving cars is a number of accidents, some of them fatal, which bear witness the engineering science that cars utilise to spot pedestrians and other obstacles and avoid collisions notwithstanding has a long way to go.
With more companies applying for permits to test driverless cars on public roads, and more public scrutiny on the tech than ever before, nosotros thought information technology best to break down how companies like Apple, Google, Uber, Tesla and others railroad train artificial intelligence to encounter the road—and which AIs might have a blind spot.
Nosotros've as well gathered the latest details on which countries allow public driverless automobile testing, which companies are developing the smartest cocky-driving artificial intelligence (AI) models, and what the future of the driverless car industry could bring in the next few years.
What is a cocky-driving car?
Simply put, a truly driverless car must be capable of navigating to a destination, fugitive obstacles, and parking without any human intervention.
To accomplish this, a driverless car must accept an artificial intelligence system that senses its surroundings, processes the visual data to determine how to avoid collisions, operates automobile mechanism similar the steering and brake, and uses GPS to track the car's current location and destination.
Without an AI, cars cannot be truly driverless.
Companies like Google'southward Waymo put have put AI inside virtual cars and have the vehicles 'drive' billions of virtual miles, throwing every perceivable obstacle and state of affairs at the cars to run across how they answer.
The AI learns what actions lead to crashes, and slowly learns how information technology should bulldoze on real roads.
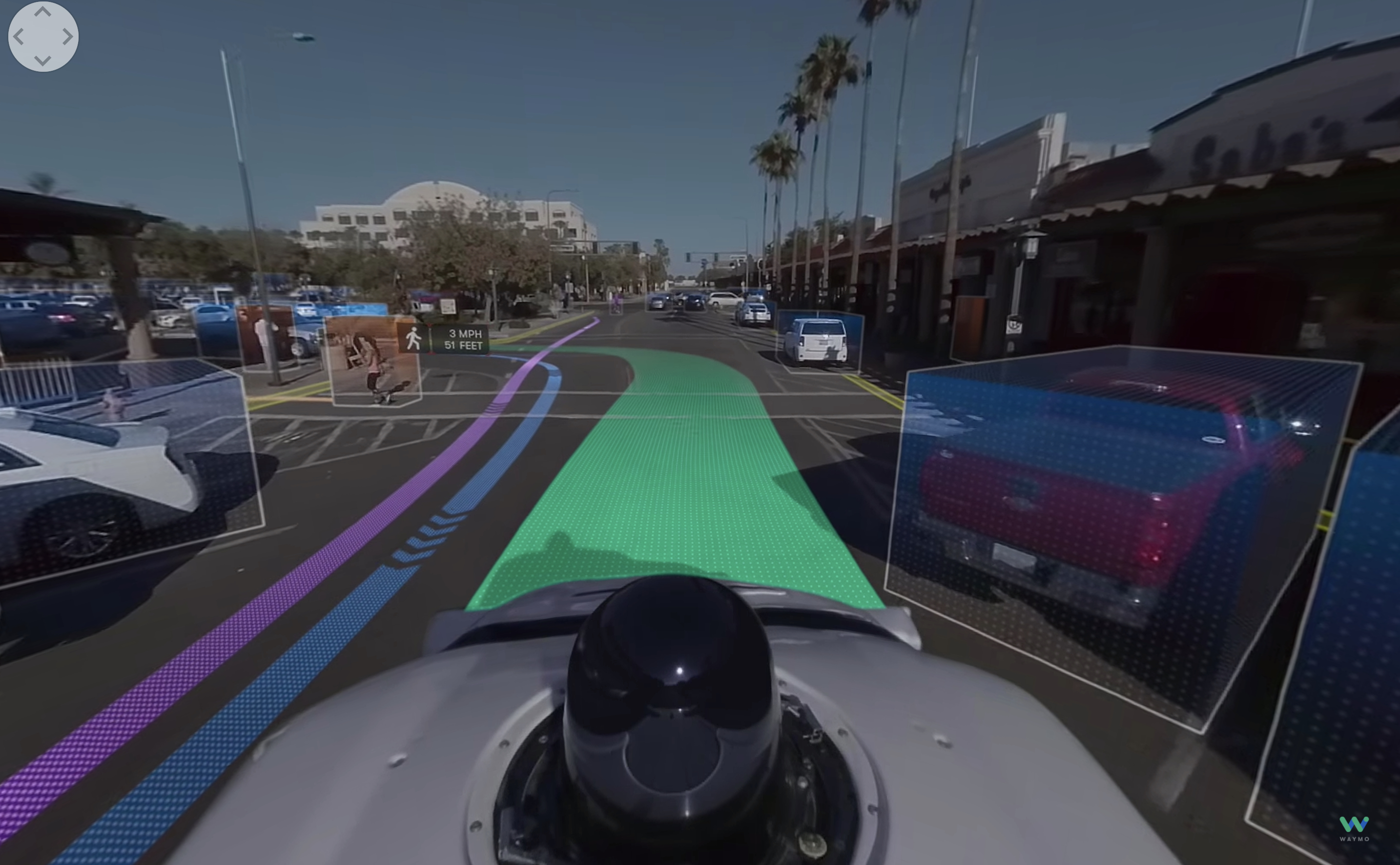

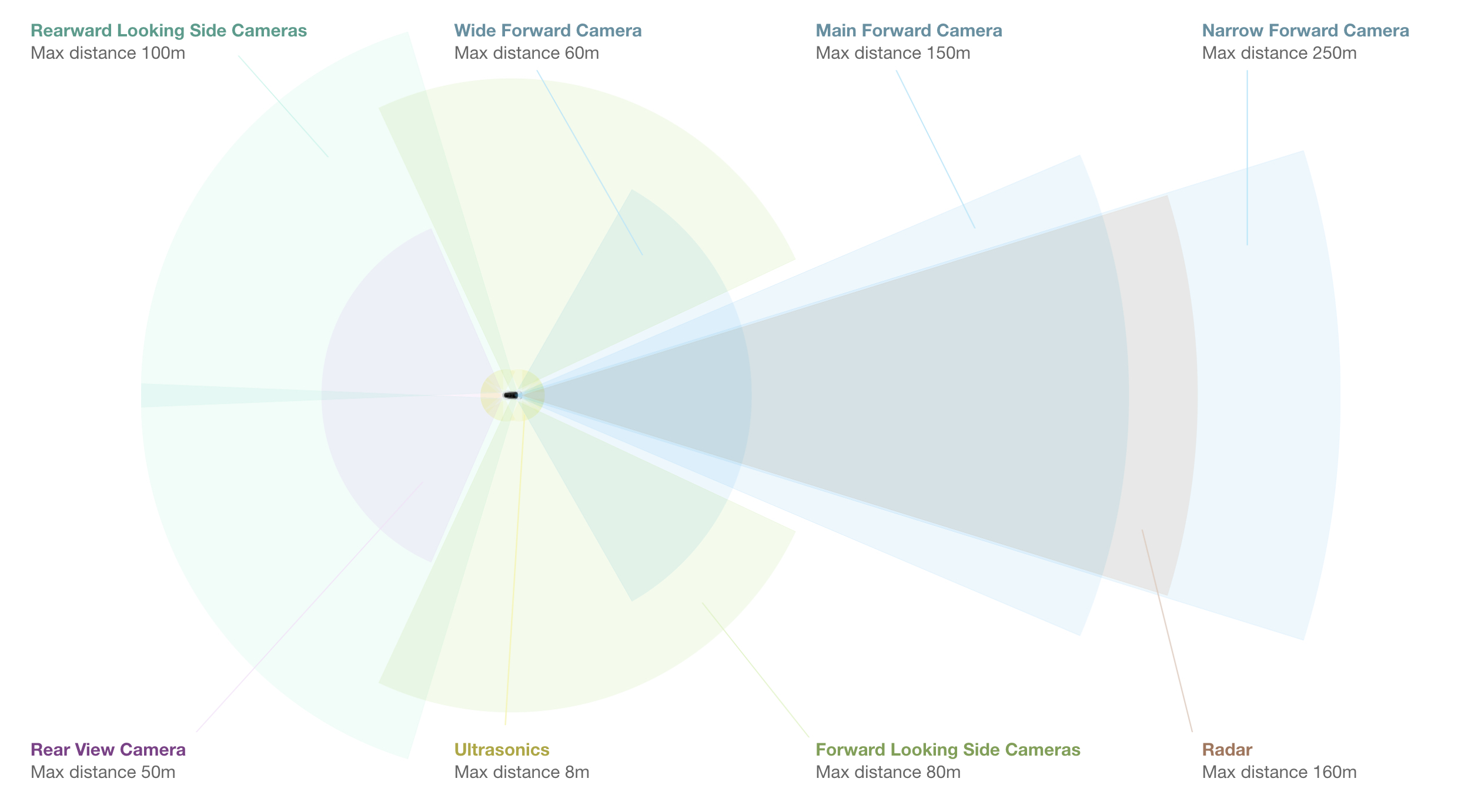
To perceive visual environment, most self-driving cars accept some combination of 3 visual systems: video cameras, radar and lidar.
The AI synthesizes the information from these different systems to fully map out its surroundings and spotter out for unexpected obstacles.
Virtually driverless cars require all iii: AIs crave visual cameras and deep learning software to interpret objects like street lights and stop signs, and while radar catches most obstacles instantly, it's not as expert as spotting smaller obstacles as lidar.
What is lidar?
Lidar sensors emit light waves in all directions; the light waves reflect off of objects and render to the sensor, measuring the distance between car and object.
Bouncing to and from the sensor millions of times in a single 2d, the lite waves create an instant, constantly updating 3D map that volition spot obstacles instantaneously.
Nevertheless, some vehicles with autonomous capabilities similar Tesla'due south Model iii don't utilise lidar; Elon Musk famously called lidar an overly-expensive "crutch", and that cameras and radar should suffice.
One thing to consider: the Model iii, along with pretty much every other "self-driving car" currently out there, aren't truly "driverless".
Nearly people tend to employ terms like "driverless", "autonomous" and "self-driving" every bit interchangeable.
But, there are significant differences in the tech required for an "autonomous" AI that tin can just handle highways and a truly "driverless" or "self-driving" car that doesn't fifty-fifty need a steering bike or human operator to park or navigate.

Some car companies tend to fog the result by claiming cruise control tech for driving straight and avoiding obstacles is "self-driving".
Mercedes-Benz actually had to pull ads that claimed its 2017 E-Class was a "vehicle that could drive itself."
But, until AI tech is sophisticated enough to drive somewhere like a school crossing without any danger to pedestrians, near, though not all, governments won't permit cars to drive without a human being seated behind the wheel.
Why should this matter to you? Because some drivers are feeling safe enough to get out the driver'south seat while their machine is in motion, putting pedestrians (and themselves) at risk. It's vitally of import that the autonomous vs driverless distinction become more clear to the public.
So, while we're covering autonomous cars in this piece, don't error them for being driverless; nearly of them accept at to the lowest degree a few years before their AIs can properly navigate the world without a human crutch.
Why do we need self-driving cars?
For commuters, the answer is obvious: a chance to take hold of some actress shut-centre, get work done or watch Netflix instead of spending hours navigating through traffic.
But why have companies invested an estimated $80 billion and years of piece of work into this technology?
For starters, it could only be a instance of jumping on the bandwagon. Pretty much every major car company has developed or implemented some kind of autopilot applied science into their cars. Not having that tech available could make a brand look out of date.
Simply, at to the lowest degree some companies have bold business concern plans for self-driving tech beyond only fitting in with everyone else.
Most car brands are very concerned with their crash safety ratings. If driverless auto tech will truly reduce the rate of accidents, auto companies volition want to push this tech frontward. AI safety ratings could fifty-fifty become a future metric for prospective car buyers to expect at.
- Tech for your auto: these are the all-time dash cams around
Ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft, meanwhile, programme to make their taxis driverless, which would mean not having to pay human drivers.
In Jan, Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi said he wanted to have cocky-driving taxis picking up passengers by 2019, and that 20% or more of Uber'southward fleet could be driverless.
However, Uber'southward cocky-driving car ambitions accept striking a major roadblock, which we'll particular farther on Pages 2 and three.
Other companies like Ford hope to contain their cars into urban center-wide networks that volition rail traffic conditions and available parking, so the visitor'southward self-driving cars volition reach destinations faster than other cars.
And so, of grade, Ford will sell its self-driving cars as a service to commitment or ride-sharing companies; Ford has already partnered with Domino's and Postmates to deliver packages and pizza in a car that'south not really self-driving, but pretends to exist in order to approximate the public's reaction.

Most of these companies don't want consumers actually ownership their self-driving cars.
But, at least one car industry expert claimed that machine companies want their driverless tech to be a "regularly recurring subscription model", where customers, even used-automobile buyers, accept to go along paying for the right non to drive.
Whatever the reasons, these companies have invested likewise much money in driverless car AIs to stop at present, despite the fact that many countries haven't fully canonical the utilize of self-driving cars still.
Businesses clearly seem to recall it's only a matter of time earlier driverless cars are on the route.
Where are self-driving cars being trialled?
While self-driving machine companies have convinced many land and national governments to allow them test their AIs on public roads, nearly all governments strictly limit the cars from driving exterior of testing tracks, with a few notable exceptions.
In the Us, 33 states have enacted legislation to let for limited cocky-driving tests, but only a few states and cities let AIs be in control on public roads—and even then almost always with strict homo oversight at all times.
The exception to this rule is Phoenix, Arizona, where Waymo has been testing self-driving cars without safety drivers on the city's streets.

Uber was too testing self-driving cars in Arizona until a high-profile fatal accident led to the country's governor to suspend Uber's testing privileges indefinitely.
Uber somewhen appear the closure of its self-driving car program in Arizona on May 23. Its program remains suspended elsewhere in the country.
California is another hot spot for self-driving cars, both considering Silicon Valley hosts so many tech companies and because California no longer requires a human behind the bike if companies can prove their AI is up to the task.
Cities in the United states where yous're well-nigh probable to spot driverless cars include Mountain View and San Francisco, California; Phoenix, Atlanta, Pittsburgh, Miami, Austin, Detroit and New York City.
Europe, habitation to several huge car manufacturers, has many receptive countries that permit for limited driverless testing.
Deutschland recently approved Volkswagen to begin testing cocky-parking cars at the Hamburg airport.
For its part, Volvo is testing driverless cars and buses in Stockholm, Sweden. In kingdom of the netherlands, Amber Mobility plans to launch a Zipcar-like service of electric driverless cars in several Dutch cities in mid-2018.

In the United Kingdom, even so, the regime recently initiated the UK Autodrive initiative to push autonomous innovation, merely, at the aforementioned time, the government is as well conducting a three-year review of self-driving engineering science'south condom implications, and hasn't canonical testing on public roads yet.
Commonwealth of australia, by contrast, has begun some public testing, but some reports say the country is lagging behind other countries in scale.
In Asia, countries like China, Japan and Singapore have enabled companies to begin testing cocky-driving taxis, but e'er with a human being backside the wheel. Uber rival Didi Chuxing is one visitor leading China'due south push button for self-driving tech.
As for self-driving tech plant in cars like Tesla's? Y'all can observe that in pretty much every nation, although most route laws dictate that drivers proceed their hands on the cycle and eyes on the road at all times.
So, who'due south making driverless cars? The respond: Everyone!
OK, that's non entirely true, and you probably desire more than details than that.
Major tech companies, from Apple tree to Google to Uber, have been working in the self-driving car space. Apple tree's cocky-driving machine was recently spotted past TechRadar, and nosotros've got a full breakup of everything having to do with the Apple Car in our in-depth guide.
Nearly all of the height-selling auto brands in the U.s.— Ford, GM, Toyota, Honda, Volkswagen, Nissan, Volvo, BMW and more than—accept been working on driverless cars for years, often in collaboration with components providers like Nvidia and Intel.
Nosotros've got the breakdown on the biggest players in the driverless car space today, plus give insight into which of them look most probable to achieve truly driverless cars in the near hereafter.
Apple tree self-driving cars
The Apple Car is a long-standing Silicon Valley rumor, and while initial reports indicated the tech giant would build its ain driverless electric vehicle, the story has inverse drastically in the final several years.
For its function, Apple has admitted that it'due south interested in creating the democratic systems that run self-driving cars, and not an actual automobile itself.
However, Apple is actively testing its cocky-driving car tech, evidenced by several car sightings in the last few years. Though the vehicles lack proprietary markings, the cars are bedecked in all the gear needed to run self-driving systems and are often seen driving around Apple office buildings and into Apple complex parking lots.
TechRadar spotted one Apple Car in May 2018 as information technology was driving on a public road and going into the parking lot of a cluster of Apple part buildings in Sunnyvale, California. The car was sporting a different-looking rig than we've seen on the vehicles previously.
Hither'southward sectional video of the Apple self-driving car we saw in May 2018
Apple tree'due south self-driving cars are coming out of the shadows and onto public roads, simply that's non all that's circulating about Apple'southward automotive projection.
In May 2018, it was revealed by the California DMV that Apple's autonomous car permit now covers 55 cars and 83 drivers, giving it the second biggest democratic car fleet in California, behind GM Cruise'south fleet of 104 and alee of Waymo's 51.
A recent patent too showed Apple'due south plans to install VR devices into its driverless cars to entertain passengers, another sign that Apple tree is working on systems for cocky-driving cars and not necessarily vehicles themselves. A second newly discovered patent describes "intent signals" as a method passengers would utilize to signal where they want the car to go.
The patent suggests a joystick, a telephone'southward accelerometer, or voice commands could be used to propose alterations to a route, choose an open parking infinite, or instruct the car to park close to a sure part of a store, like near a specific archway.
All of this points to Apple's interest and active development in the driverless car space. We wouldn't be surprised to see Apple's self-driving project come to light in the side by side one to iii years.
Google'south driverless cars
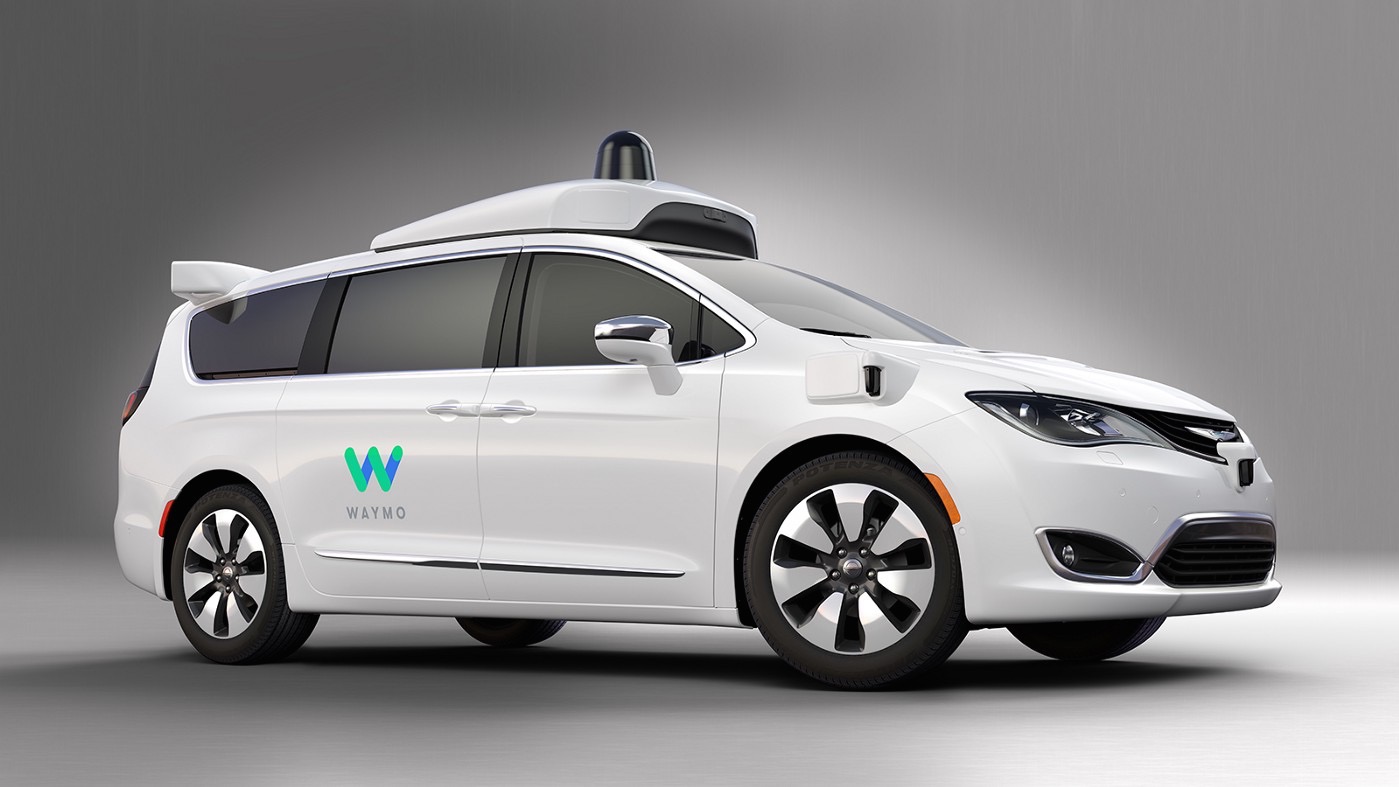

Waymo, the cocky-driving automobile segmentation of Google'southward parent company, Alphabet, was formally launched in late 2016, just its self-driving tech has been in development since 2009.
And that nigh-decade of work has paid off in arguably the most reliable driverless auto nosotros've seen to date.
Detachment—when a human driver has to take command of a self-driving motorcar—is the chief metric by which automakers gauge their self-driving AI's technical skill. And Waymo's cars pb the pack: Waymo self-driving cars disengage 0.18 times every one thousand miles.
For context, if a Waymo car drove beyond the United states of america and back, a human would on boilerplate take to intervene in one case. Only GM's self-driving cars come close to that level of disengagement, averaging about 1,000 fewer miles per disengagement.
How has Waymo'southward team attain this level of reliability? With a powerful organization of vi lidar sensors that instantly detect any potential hazards, and a deep learning organisation sophisticated plenty to respond instantly to obstacles and weather hazards.
Waymo collects its lidar, radar and camera feed information into an aggregate map of the surrounding road, which the company calls x-view.
The video higher up shows a stylized version of how 10-view can detect people and avoid accidents.
Waymo's cars take driven six million miles on public roads thus far, along with 2.seven billion virtual miles inside of traffic simulators.
Sometimes the car's power to bulldoze itself can't keep information technology out of every accident though, equally was seen in Arizona in 2018 when an oncoming car swerved across the route and crashed into a Waymo van, injuring the test commuter inside.
Still, Waymo hopes to add together to its armada's mileage on public roads in the next couple of years, equally it rigs xx,000 new all-electric Jaguar I-Footstep cars and an immense 62,000 Fiat Chrysler minivans with Waymo AI tech congenital in.
Waymo'due south partnership with Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) could eventually mean cocky-driving FCA-built vehicles becoming available directly to consumers.
Waymo's bold goal is to launch a "driverless ride-hailing service" in Phoenix in 2018, and eventually expand nationwide.
Waymo has recently been eyeing Europe as some other expanse for expansion, simply it may need to rely on strategic partnerships to be competitive there. Waymo's parent company Alphabet has a shaky human relationship with the EU, and it lacks the brand recognition and loyalty that its European competitors accept.
We'll have to wait and see if Uber's fatal self-driving car crash in Arizona or Waymo's own standoff stall any of the company'south plans, yet.
Uber's driverless cars
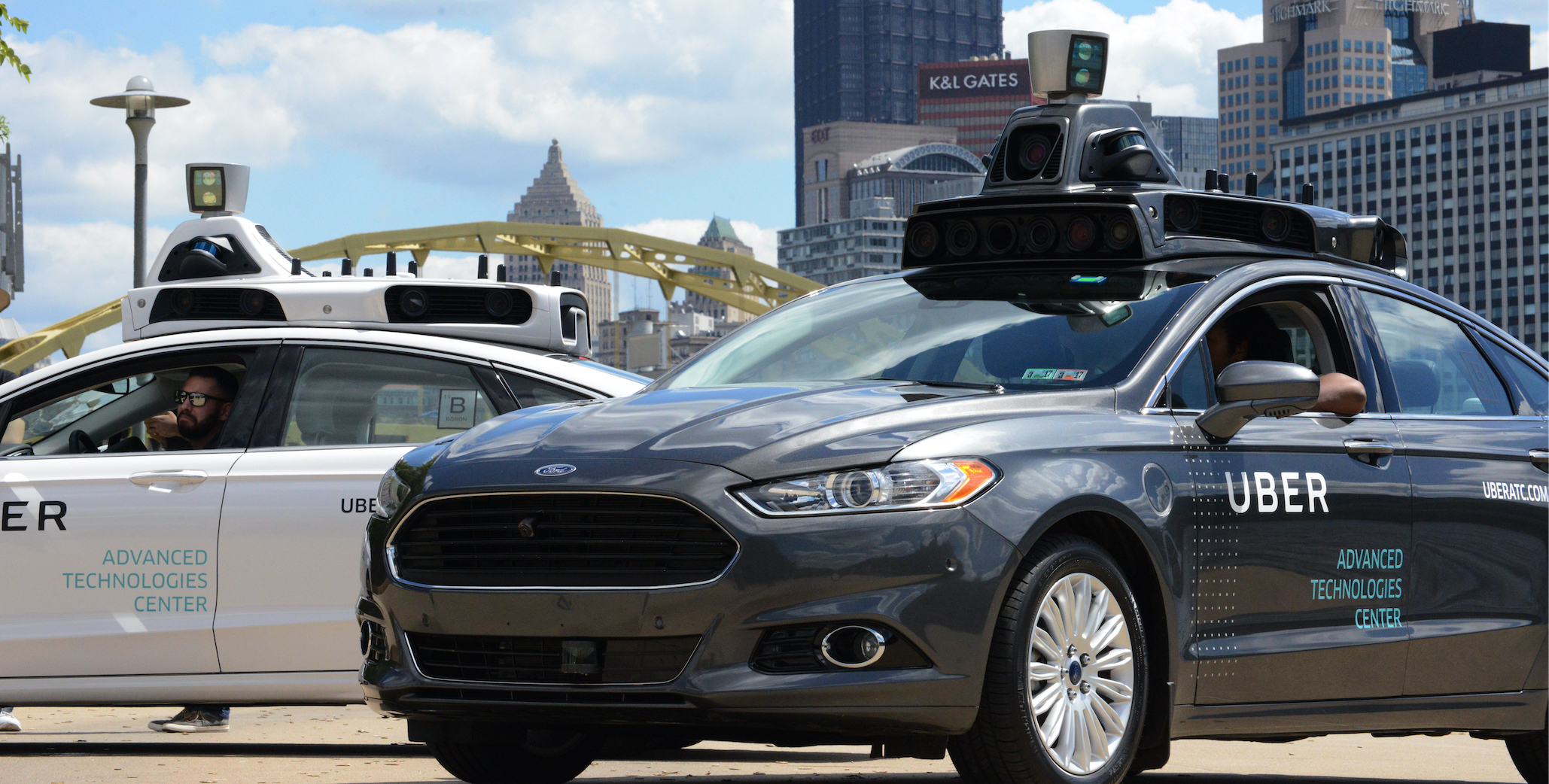

Uber's relatively late offset to the self-driving game hasn't stopped the ride-sharing company from zealously testing its AI tech on public roads, hoping to beat Waymo to the punch and outset its ain driverless taxi service.
After purchasing Otto, a self-driving truck company in 2015, Uber's ATP developed its own system of cameras, radar and lidar to rail obstacles, using a Nvidia GPU to ability its AI tech.
ATP reportedly settled on just one lidar sensor, compared to Waymo'due south vi, to install on its 24,000 Volvo XC90 SUVs.
Uber'southward cocky-drivings machine have driven over one meg miles on public roads, though its detachment statistics don't stack upward to Waymo's: Uber reportedly simply makes it xiii miles on average before a human must arbitrate.
Though it began with gusto, Uber's self-driving car plan is currently in limbo. After a fatal blow in Arizona in March 2018, the state's governor suspended Uber's ability to test cocky-driving cars in the state. Uber had already close downward tests nationwide post-obit the blow.
And then, in May, Uber announced information technology was shutting down its self-driving car plan in Arizona completely. It will continue tests in San Francisco, Toronto and Pittsburgh, whenever tests resume.
When Uber'south tests brainstorm once again, they volition be in a much more express fashion than earlier. As far every bit when they start again, Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi hopes to run into his autonomous armada driving in the next couple months.
Uber plans to take findings from the National Transportation Safety Board's (NTSB) investigation into the fatal accident to make changes to its programme. The company is also undergoing an internal safety review.
The preliminary NTSB written report reveals that while the vehicle had an automatic emergency braking feature, this was disabled because the car was in "computer mode." Citing Uber, the written report says the feature is disabled to forestall erratic driving beliefs.
Though the machine detected it needed to brand an emergency braking maneuver i.3 seconds before it struck the pedestrian who later died of her injuries, the arrangement doesn't alert the driver to have control of the vehicle.
You can read more on what is in the initial NTSB written report into the fatal Uber self-driving auto crash here.
In light of the accident and subsequent fall-out, Uber'south contributions to the driverless machine industry have been overshadowed.
Work that Uber had washed included patenting a fashion to prevent motion sickness in passengers with a "Sensory Simulation System" that would suit seats, air flow and in-motorcar lighting to brand riders more than comfortable.
In another patent, Uber outlined how its cars could signal pedestrians or cyclists with flashing lights or a bumper text brandish—"intention outlets" that would help cars experience less inscrutable and difficult to predict.
What'south more than, Uber has developed an democratic truck service that volition make freighting goods beyond the country much easier for truck drivers.
Despite the work that it'south done in the self-driving motorcar space, Uber has a big uphill battle before the public trusts its democratic vehicles once more.
One fashion Uber is eyeing as a means for getting democratic vehicles on the road without as nifty of safety concerns is past partnering with Waymo. Uber's CEO has said the companies are in talks, trying to bring some of Waymo's vehicles to Uber's driverless car fleet. Notwithstanding, given Uber and Waymo's past legal battle over trade clandestine theft, the grounds for a new partnership seem shaky.
Tesla'southward driverless cars

Tesla Model X, Model Ten and Model 3 cars all feature the latest version of Autopilot, a sensor system of cameras, sonar and radar congenital for autonomous driving on highways.
Tesla's AI tin perform tasks like preemptively shift lanes earlier an exit or to avoid slower traffic, and tin autosteer around more windy highways.
Once you leave the throughway, your car will warn you to have control of steering.
Equally of early 2016, Tesla owners had allegedly driven hundred of millions of miles in Autopilot mode. And, considering Tesla scrapes data from all of its cars, it's able to gather information on apparent errors to improve Autopilot over time. That dwarfs the mere millions of public road miles that near cocky-driving cars have achieved.
Of course, Tesla'south miles are autonomous, non driverless.
Tesla does sell models with "full self-driving capability" on its website, but these models apparently take only double the cameras as a regular Tesla and no other major changes.
Moreover, Tesla admits that enabling this mode would require "extensive software validation and regulatory approval" that isn't yet available.
Withal, many drivers tend to treat Autopilot like a self-driving way rather than equally a commuter aid systems, which has led to serious accidents, including in recent months.
One recent crash killed a Tesla Model X commuter when his machine crashed on a freeway in California. The driver had ignored Autopilot's warnings to assume control of the vehicle. The NTSB is still investigating the crash.
Bated from some other high-profile crashes, Tesla insists that its Autopilot and Autosteer tech generally lead to a 40-l% reduction in accidents. The below tweet shows how its tech can pick up on potential hazards most humans might miss.
Original video, potency from the owner. Essential, no one could predict the blow but the radar did and acted past emergency braking. pic.twitter.com/70MySRiHGRDecember 27, 2016
For now, Tesla hasn't announced whatsoever recent news on true driverless tech, and no one has spotted any cocky-driving patents by the company, either.
It's unclear if Tesla is playing things close to the chest, or if information technology's content sticking with what information technology's done so far while other companies duke it out over more challenging AI goals.
The other major players

Outside of these 3 major players, many other companies are maneuvering to advance public testing, or even launch for-profit driverless automobile services, in the adjacent few years.
Full general Motors, the runner-up to Waymo in AI reliability, plans to start testing its cars in Manhattan this year.
New York is something of an Everest for self-driving companies to climb: edifice an AI capable of navigating the city's traffic and hoards of pedestrians is no easy task.
GM's fully automated Chevy Volts each have a $v one thousand thousand insurance policy for any potential crashes, and tin can't enter any school or structure zones.
If the cars can pass this gauntlet, GM'south AI could exist powerful plenty for the Chevy Cruise AV, a truly driverless machine without a steering wheel or gas pedal.
But, GM isn't going to tackle this claiming alone. Japanese company SoftBank is offering $two.two billion in backing to GM for a 20% stake in GM's cocky-driving department. Of that money, $1.35 billion is withheld until GM's autonomous vehicles are commercially ready.
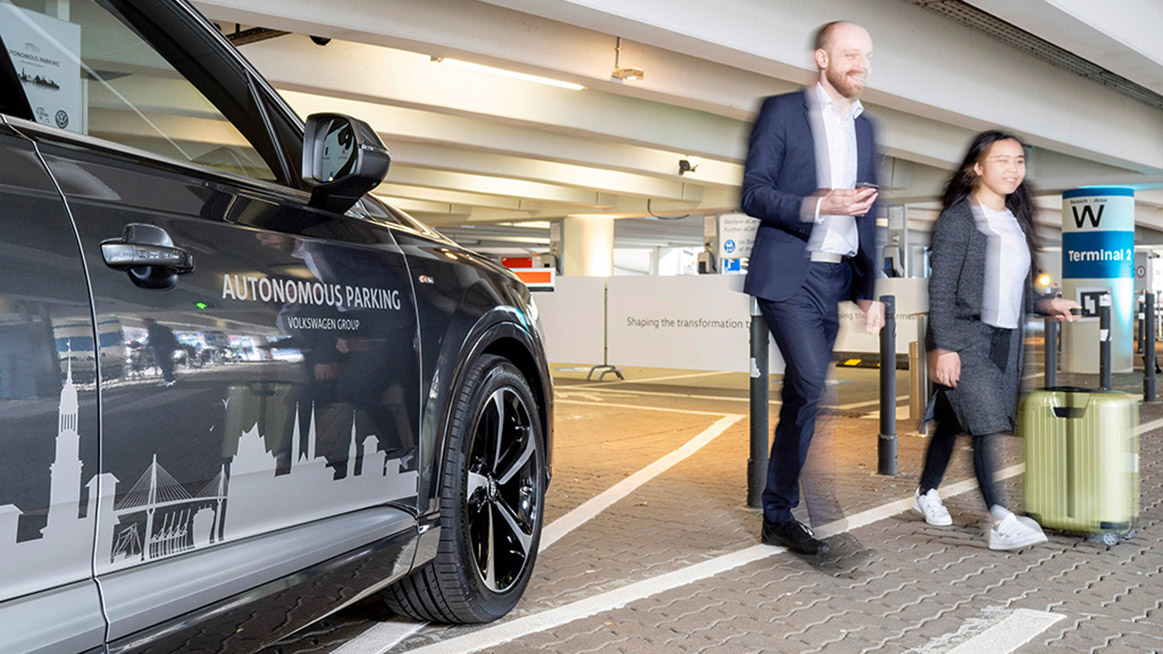

Volkswagen, conversely, is braving the chaotic battleground known as parking garages for its testing.
At the Hamburg Aerodrome in Federal republic of germany, VW machine owners can simply driblet off their cars in front of the garage and activate a smartphone app; the motorcar then cocky-drives to a gratis parking space, using its GPS and cameras to navigate.
Eventually, VW has designs to make your driverless automobile maintain itself, and even exercise your chores. The company stated how its cars will be able to speak with urban center systems to find free parking, or bulldoze themselves to gas stations or car washes for service.
Other big proper noun car companies oasis't made their plans public for driverless cars, just practise have dates in listen for when their AI tech will be ready.
Hyundai hopes to have its cars fully driverless on the road by 2021, and Ford also aims to have its driverless AI and traffic-tracking technology up and running in the same year.
Meanwhile, Google's rivals in the smartphone industry also accept aspirations to take the search behemothic on in the self-driving industry.
Samsung recently got permission from the California DMV to test democratic vehicles.
And even Huawei has jumped into the game, showing off a self-driving machine before this yr that ran entirely off of camera information from a smartphone.
Finally, Lyft hopes to shell Uber at its own game. Lyft launched its own self-driving segmentation final year, and have since teamed up with Ford and acquired the aid of an automotive parts supplier, Magna, for its self-driving auto machinery.
With so many companies hoping to launch self-driving services and ramp up testing in the adjacent couple of years, driverless car tech must be up to the challenge to avoid a rise in accidents as a upshot.
Both Uber and Tesla accept recently been embroiled in scandals surrounding their self-driving AI later on two fatal accidents this year.
Beneath, we've laid out the most high-contour accidents to take identify in the driverless car manufacture then far.
After this, y'all'll notice our predictions how the manufacture could abound in the side by side few years—if accidents don't derail it entirely.
Self-driving car accidents
In 2016, when Autopilot was however newly implemented technology, a Tesla enthusiast fatally crashed into a trailer while Autopilot was engaged.
At the time, there was awareness that Autopilot had problem picking up trailers on its cameras, but nothing had been washed to set the issue before the crash.
The incident was investigated by the United states's NTSB, which initially said Tesla'southward AI wasn't at fault but eventually stated in 2017 that Autopilot's "operational limitations" played a role in the accident.
The agency warned that drivers using the arrangement became too complacent to reply to any potential threats.
That pattern would somewhat repeat itself in a fatal 2018 blow, when a Tesla Model X driver crashed into a concrete bulwark while using Autopilot.
According to Tesla, "The driver had received several visual and one audible hands-on warning earlier in the bulldoze and the driver's easily were non detected on the wheel for six seconds prior to the collision".
The NTSB is also investigating this incident, and expressed displeasure that Tesla released its own results of the crash before the NTSB could publicly make its own argument. Tesla CEO Elon Musk claimed he had a duty to tell his customers the truth for safety reasons.
Lot of respect for NTSB, simply NHTSA regulates cars, not NTSB, which is an advisory body. Tesla releases disquisitional crash information affecting public rubber immediately & e'er will. To do otherwise would exist dangerous.Apr two, 2018
Prior to this blow, an Uber machine with driverless engineering struck a pedestrian as she walked exterior of a crosswalk at dark. This fatal collision led to Uber suspending all of its cocky-driving operations indefinitely.
As with Tesla, the NTSB investigation of the crash is yet ongoing, though the agency's preliminary written report into the accident has been issued.
Some incredibly sorry news out of Arizona. Nosotros're thinking of the victim'due south family equally we work with local police force enforcement to understand what happened. https://t.co/cwTCVJjEuzMarch nineteen, 2018
As for Google'southward most loftier-profile incident, it happened in March 2016 when a self-driving Lexus SUV attempted to make a turn in front of a charabanc, with the automobile's AI assuming the bus would tiresome downward to allow it to do so.
Nevertheless, the omnibus didn't stop, and the Google self-driving car struck the bus'due south side at 2 mph.
In its monthly DMV report, Google detailed the crash, and said it had adjusted its AI'due south parameters to recognize that omnibus drivers are less likely to give right-of-way.
Most recently, a self-driving Waymo minivan was involved in an accident in May 2018, in Chandler, Arizona. Simply in this case, Waymo's AI was not to be blamed for the incident.
According to the Chandler Police department, a Honda sedan ran a carmine light, then collection into oncoming traffic to avoid some other car in an intersection, swerving directly into the Waymo minivan's path. The human commuter backside the wheel suffered small-scale injuries.
Waymo released footage of the incident, which makes it articulate that neither the AI nor the human operator could take reasonably predictable the crash.
Local police force initially claimed that Waymo's auto had been in autonomous way at the time of the crash, merely later on affirmed Waymo'south assertion that the automobile had been in manual mode, and they stressed from the showtime that neither Waymo nor the SUV commuter was considered at fault for the incident.

Speaking with Forbes following Uber'due south fatal accident, Waymo CEO John Krafcik said that, "We're very confident that our car could have handled that situation."
Waymo will probably confront significant backlash if information technology does face a serious accident of its ain afterward Krafcik's bold merits.
Of form, nosotros'll take to expect until authorities conclude their investigations into the recent self-driving car accidents earlier we can fully assess how safe the tech is and what steps need to be taken to avert hereafter accidents.
What does the time to come hold?
The history of the driverless car industry has been ane of bold promises, high-profile fiascos, and full general doubtfulness well-nigh the future.
It's truly unclear whether governments will ever let cocky-driving cars operate without a human being operator on a national level, though it seems we are steadily moving in that direction.
A research squad establish that deep learning networks in self-driving cars are decumbent to make thousands of incorrect choices when faced with tricky scenarios.
The researchers are hoping to develop a more than complete test for self-driving car companies to check whether their AIs tin can navigate these problems. Merely, in the meantime, more accidents could be in shop.

Nonetheless, while accidents will play a big role in the industry's prospects, perhaps the most of import event volition exist whether self-driving cars bear witness to be condom not but from AI malfunctions, but also malicious AI attacks.
A recent written report called The Malicious Employ of Artificial Intelligence, written by bookish researchers and Elon Musk'due south OpenAI watchdog group, detailed how hackers could infiltrate the AI of a self-driving network and cause cars to ignore safety laws.
Without protections in place, driverless cars could even become weaponized for potential attacks. The researchers recommended that companies work with one another and with lawmakers to preempt potential hacking vulnerabilities.
Will rivals like Waymo and Uber be willing to share such data, or will they hoard information technology? I can hope that companies will encounter the benefits of working together for the well-being of all.
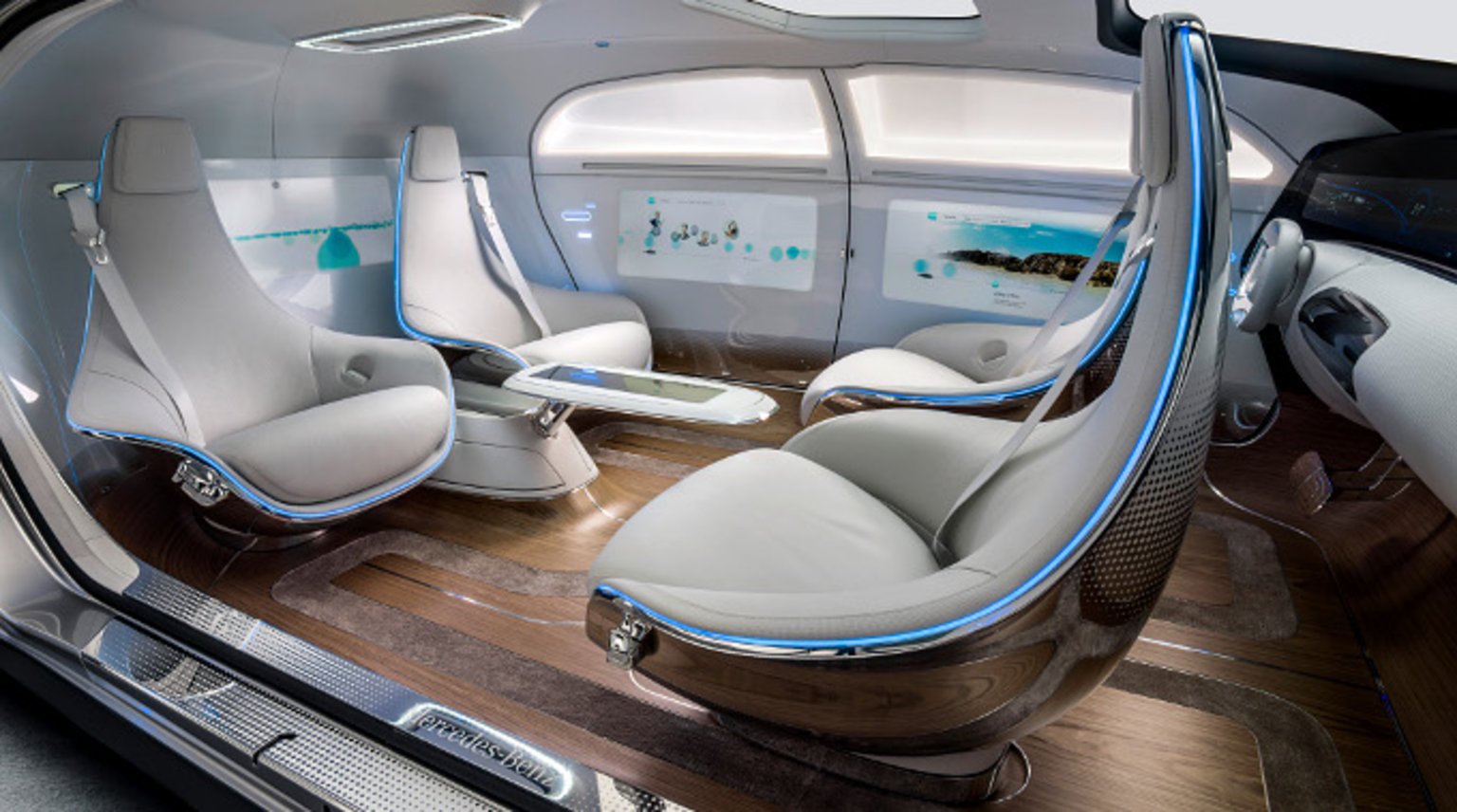

If self-driving cars do take off, though, nosotros can expect a future where companies rely more frequently on autonomous tech, potentially at the expense of jobs. Amazon, for example, hopes to lower shipping costs by employing driverless commitment vehicles.
If anything is uncertain, information technology'south whether you or I will own self-driving cars of our ain. A collection of ride-sharing companies—ZipCar, Uber, Citymapper, Lyft and BlaBlaCar—all released a policy certificate recommending that "autonomous vehicles (AVS) in dumbo urban areas should be operated only in shared fleets."
It'south possible that self-driving car companies will continue to vestibule governments for "shared fleet" exclusivity, and so that you can just subscribe to their self-driving services instead of owning your ain vehicle.
Of course, car manufacturers similar GM and Ford will likely want to sell their cocky-driving cars to consumers directly, and then they might lobby against such proposals.
Ultimately, with billions of dollars invested, nosotros believe these companies will likely make driverless cars a commonplace reality within the next decade—though the road there might exist littered with legislative speed bumps and public distrust.
Regardless, go set up for hereafter generations to roll their eyes when you talk about how, dorsum in your twenty-four hours, y'all had to bulldoze to work yourself.
- Everything y'all need to know virtually electric vehicles
Source: https://www.techradar.com/news/self-driving-cars
Posted by: hooperseliesser.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can You Register Your Vehicle For One Year At A Time In Maryland"
Post a Comment